Als Datenquelle für die Zugangsdaten wird eine Datenbanktabelle verwendet.
...
Pflichtfelder - Folgende Datenfelder müssen vorhanden sein:
...
A database table is used as data source for the access data.
- Name of the database table - The table name can be chosen freely, usually USER.
Required fields - The following data fields are obligatory:
Von RapidClipse generierte DatenstrukturRequired fields Data type Explanation USERNAME String Saves the username as a string. PASSWORD byte[] Speichert das Passwort als Byte-Array, i.d.R. verschlüsselt. Saves the password as a byte array, usually encrypted. Data structure generated by RapidClipse
Entities
AttributeDatentyp Data type ErklärungExplanation username StringSpeichert den Benutzernamen als String Saves the username as a string. password byte[] Speichert das Passwort als Byte-Array, i.d.R. verschlüsselt.Saves the password as a byte array, usually encrypted. Data Access
UserDAO
RoleDAO
ResourceDAO
- Weitere Datenfelder - Die USER Tabelle kann bei Bedarf auch weitere Datenfelder enthalten, da diese für die Authentifizierung nicht relevant sind. Häufig benötigte Informationen zu einem Benutzer sind u.a. E-Mail, Status (aktiviert oder deaktiviert), Foto, Zeitzone, Letzte Session, IP-Addresse, URL zu einer Log-Datei etc.
- Umgang mit vorhandener USER Tabelle - Ist in Ihrer Datenbank bereits eine Tabelle für die Verwaltung von Benutzern vorhanden, stellen Sie sicher, dass für diese ein entsprechendes Entity mit dazugehörigem DAO in Ihrem Project Management unter Entities bzw. Data Access vorhanden ist. Falls nicht, können Sie das fehlende Entity und DAO mit der Import-Funktion Create JPA entities from table generieren lassen. Abweichende Tabellen- und Datenfeldnamen stellen auf Grund des später durchgeführten Mappings kein Problem dar.
...
- Additional data fields - If required, the USER table can also include other data fields, since they are not relevant for authentication. Frequently used information about a user include e-mail, status (enabled or disabled), image, time zone, last session, IP address, URL for a log file, etc.
- Dealing with an existing USER table - If you already have a table for managing users in your database, make sure that there is an appropriate entity with corresponding DAO in your Project Management in Entities or Data Access. If not, you can generate the missing entity and DAO with the Create JPA entities from table import function. Different table and field names are no problem because the mapping is performed later.
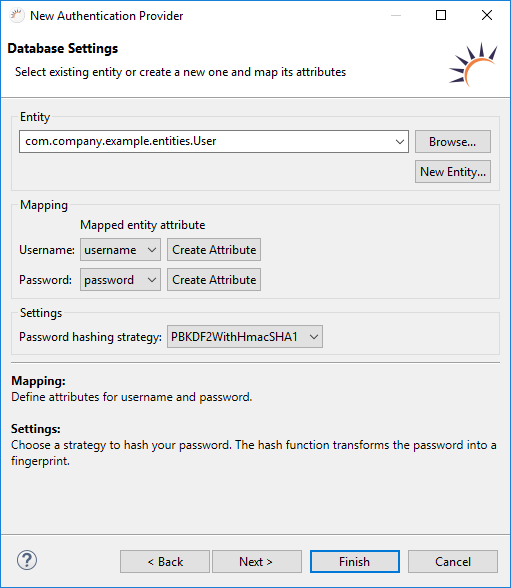
- User Entity already exists - Select your existing User entity.
No User Entity available yet - Click /wiki/spaces/DOC/pages/31850645 um ein neues Entity User inklusive DAO UserDAO anzulegen. - Wählen Sie bei Mapping > Username das Attribut für den Benutzernamen aus.
- Wählen Sie bei Mapping > Password das Attribut für das Passwort aus.
- Wählen Sie bei to create a new User entity, including the UserDAO DAO.
- Select the attribute for the username under Mapping > Username.
- Select the attribute for the password under Mapping > Password.
- Select the encryption algorithm for the password under Settings > Password hashing strategy den Verschlüsselungs-Algorythmus für das Passwort aus, z.B, e.g. PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1.
- Klicken Sie auf Click Finish.
Weiter mit Autorisierung
/wiki/spaces/DOC/pages/31850703 - Für das neue Entity User muss eine entsprechende Tabelle USER in der Datenbank angelegt werden. Dafür bietet Ihne RapidClipse eine Export-Funktion.
...
Go to authorize
Create database table USER - A corresponding table has to be created for the new User entity in the USER database. For this, RapidClipse offers an export feature.
Options:
Mapping
Username - Auswahl des Attributs für den BenutzernamenSelection of the attribute for the user name.
Password - Auswahl des Attributs für das PasswortSelection of the attribute for the password.
- Password hashinig hashing strategy
MD5 - Message Digest Algorithm ist eine Hashfunktion, die aus einem Passwort einen 128-Bit-Hashwert erzeugt. Gilt jedoch als nicht mehr sicher The message digest algorithm is a hash function that creates a 128-bit hash value from a password. However, this is no longer considered secure.
Code Block language java theme Confluence // Example RapidClipse cb9086f37a2e96bd5e4507f869888261
SHA1 - The Secure Hash Algorithm 1 ist eine Hashfunktion, die aus einem Passwort einen 160-Bit-Hashwert erzeugtis a hash function that creates a 160-bit hash value from a password.
Code Block language java theme Confluence // Example RapidClipse 64d88c018c7ced7e248e42b48593bd82c5e80ef2
SHA2 - The Secure Hash Algorithm 2 ist der aktuell empfohlene Standard für SHA, die aus einem Passwort einen is the currently recommended standard for SHA that creates a 224-, 256-, 384- oder or 512-Bit-Hashwert erzeugtbit hash value from a password.
Code Block language java theme Confluence // Example RapidClipse eafa795b8ffea05d1c8a7d5142bd4dd50fea3dd447f3585071e5c8b2ef525cef
PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1 - Kombination aus Combination of PBKDF2, HMAC und SHA1, die einen 160-Bit-Hahswert erzeugtand SHA1 which creates a 160-bit hash value. PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) ist eine genormte Funktion für die Ableitung eines Schlüssels aus einem Passwort und wird oft für die passwort-basierte Authentifizierung benutztis a standardized function for deriving a key from a password and is often used for password-based authentication. HMAC (Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code) ist ein is a Message Authentication Code (MAC), dessen Konstruktion auf einer kryptografischen Hash-Funktion basiert. SHA1 ist eine Hashfunktion, die aus einem Passwort einen 160-Bit-Hashwert erzeugt. the construction of which is based on a cryptographic hash function. SHA1 - is a hash function that creates a password from a 160-bit hash value.
Code Block language java theme Confluence // Example RapidClipse eafa795b8ffea05d1c8a7d5142bd4dd50fea3dd447f3585071e5c8b2ef525cef
...
Result:
Project Management > Entities - Es wird die Entity-Klasse The User.java mit den Attributen username vom Typ String sowie password vom Typ byte[] generiert oder durch Auswahl ein bereits existierendes Entity verwendet entity class is created with the attribute username of the type string and the attribute password of the type byte[] or by selecting an existing entity.
Entity AttributeDatentyp Data type ErklärungExplanation User username StringSpeichert den Benutzernamen als String Saves the username as a string. password byte[] Speichert das Passwort, i.d.R. verschlüsselt als Byte-Array.Saves the password, usually encoded as a byte array. Project Management > Data Access - Es wird die DAO-Klasse The UserDAO.java generiert. Bei Auswahl eines bereits existierenden Entities wird kein neues DAO generiert DAO class is generated. When selecting existing entities no new DAO is generated.
Project Management > Business Objects - Es wird die Klasse The ExampleAuthenticationProvider.java generiert class is generated.
Code Block language java theme Confluence package com.company.example.business; import com.company.example.entities.User; import com.xdev.security.authentication.Authenticator; import com.xdev.security.authentication.AuthenticatorProvider; import com.xdev.security.authentication.CredentialsUsernamePassword; import com.xdev.security.authentication.jpa.JPAAuthenticator; import com.xdev.security.authentication.jpa.HashStrategy.PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1; public class ExampleAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticatorProvider<CredentialsUsernamePassword, CredentialsUsernamePassword> { private static ExampleAuthenticationProvider INSTANCE; public static ExampleAuthenticationProvider getInstance() { if (INSTANCE == null) { INSTANCE = new ExampleAuthenticationProvider(); } return INSTANCE; } private JPAAuthenticator authenticator; private ExampleAuthenticationProvider() { } @Override public Authenticator<CredentialsUsernamePassword, CredentialsUsernamePassword> provideAuthenticator() { if (this.authenticator == null) { this.authenticator = new JPAAuthenticator(User.class); this.authenticator.setHashStrategy(new PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1()); } return this.authenticator; } }
Example:
Passwort verschlüsselt speichernSave encrypted password
Code Block language java theme Confluence String password = this.passwordField.getValue(); byte[] encryptedPassword = new HashStrategy.SHA2().hashPassword(pw.getBytes()); User user = new User(); user.setPassword(encryptedPassword); try { new UserDAO().save(user); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception }
...
Note:
- Passwort speichern und editieren - Formulare werden üblicherweise sowohl für Speichern und Editieren von Daten verwendet. Für das Speichern und Editieren von Passwörter müssen Sie jedoch unterschiedliche Formulare erstellen. Denn beim Speichern wird das Passwort verschlüsselt in die Datenbanktabelle geschrieben, sodass Sie beim lesenden Zugriff immer ein verschlüsseltes Passowrt erhalten. Ein erneutes Speichern, würde das bereits verschlüsselte Passwort ein weiteres Mal verschlüsseln und dadurch ungültig machen.
- Passwörter manuell in Datenbanktabelle eintragenSave password and edit - Forms are commonly used for both storing and editing data. However, for storing and editing passwords, you need to create different forms. When saving, the password is entered into the database table encrypted so that you will always receive an encrypted password during reading access. Re-saving would encrypt the already encrypted password again and thus it would be invalid.
- Enter passwords in the database manually