To implement the authorization, you need three tables for managing users, roles, and rights in the database, each of which is connected to the others by an n:m relation. The wizard allows you to generate the appropriate entities. In addition, the entities are connected by mapping. This allows RapidClipse to handle entities and attributes of any name. If the default mapping does not match your data structure, you can define custom queries.
Even if you use the authentication via LDAP, you have to save the users in a database table to connect users and roles with each other. Users and roles must be synchronized at runtime.
Required data structure in general
Users - Save username, password, and any additional user-specific information. The designations used in RapidClipse APIs are User and Subject.
Roles - Save the roles/groups to which a user can belong. The designations used in RapidClipse APIs are Roles, Usergroups, and Userroles.
Rights - Save rights that can have a role. Here, you can also save the states or conditions that must be met. The designations used in RapidClipse APIs are Permissions and Resources.
Data structure generated by RapidClipse
Entities
Entity Attribute Data type Explanation User username String Saves the username as a string. password byte[] Saves the password as a byte array, usually encrypted. roles Set / List List of all roles. Role name String Saves the name of the rolls as a string. resources Set / List List of all rights. childRoles Set / List List of all roles. parentRoles Set / List List of all roles. users Set / List List of all users. Resource name String Saves the name of the rights as a string.. roles Set / List List of all roles. Data Access
UserDAO
RoleDAO
ResourceDAO
Database tables (using the example of MySQL) - Database tables generated by the (Hibernate) entity export function.
Entity Data fields Data type Explanation USER USERNAME varchar(255) Saves user data, including username and password. password tinyblob ROLE NAME varchar(255) Saves all roles. RESOURCE NAME varchar(255) Saves all rights. ROLERESOURCENM ROLE varchar(255) Saves all role-right combinations. A role can have many rights, a right can occur in many roles. RESOURCE varchar(255) ROLEROLENM CHILDROLE varchar(255) Saves any role-role combination, thus allowing the nesting of roles. PARENTROLE varchar(255) USERROLENM USER varchar(255) Saves all user-role combinations. A user can have many roles, a role can be taken by many users. ROLE varchar(255)
Dealing with an existing USER table: If you have already developed a table for managing users, roles, and rights in your database, make sure there is an appropriate entity with corresponding DAO in Project Management in Entities or Data Access. If not, you can generate the missing entity and DAOs using the Create JPA entities from table import function. It is not a problem if the field and table names are different because mapping is performed later.
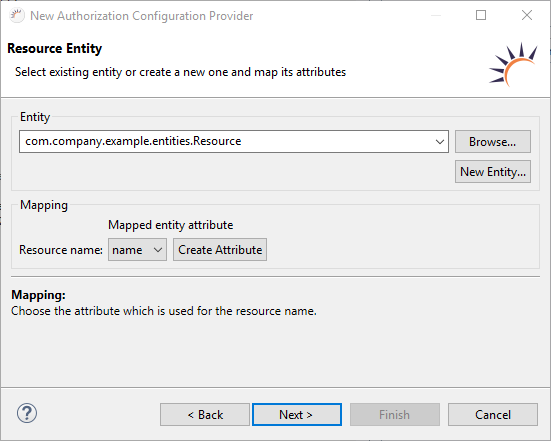
Define/generate resource table
- Entity for rights already exists: Select your existing entity.
No Resource Entity available yet: Click New Entity... to create a new Resource entity, including ResourceDAO DAO. - Select the respective attribute for the user rights Mapping > Resource name.
- Click Next >.
Options:
Resource name - Select the attribute to which the resource name is mapped for the user rights
Note:
Mapping - Once you have generated the Resource entity, you can apply the specified Resource.name attribute.
Result:
Project Management > Entities - The Resource.java entity class is generated or used by selecting an existing entity.
Entity Attributes Data type Resource name String Project Management > Data Access - The ResourceDAO.java DAO class is generated. When selecting existing entities no new DAO is generated.
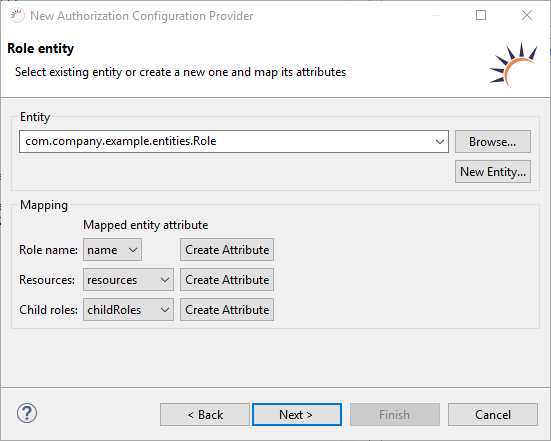
Define/generate roles table
- Table for roles (Roles) already exists - Select your existing Role entity.
No role entity exists yet - Click New Entity... to create a new Role entity including the RoleDAO. - Select the attribute for saving the roles under Mapping > Role name.
- Select the attribute for saving the rights under Mapping > Resources.
- Select the attribute for saving the sub roles in Mapping > Child roles.
- Click Next >.
Options:
Role name - Auswahl des Attributs für die Bezeichnung der Rollen.
Resources - Auswahl des Attributs mit der Liste (Set/List) aller Rechte für eine Rolle.
Child roles - Auswahl des Attributs mit der Liste (Set/List) aller Unterrollen für eine Rolle.
Hinweis:
Mapping - Wenn Sie das Entity Role generieren lassen, können Sie die vorgegebenen Attribute übernehmen.
Ergebnis:
Project Management > Entities
Role - Es wird die Entity-Klasse Role.java generiert oder durch Auswahl ein bereits existierendes Entity verwendet.
Entity Attribute Datentyp Role name String resources Set / List childRoles Set / List parentRoles Set / List Resource - Die Entity-Klasse Resource.java wird um das Attribut roles erweitert.
Entity Attribute Datentyp Resource name String roles Set / List
Project Management > Data Access - Es wird die DAO-Klasse RoleDAO.java generiert. Bei Auswahl eines bereits existierenden Entities wird kein neues DAO generiert.
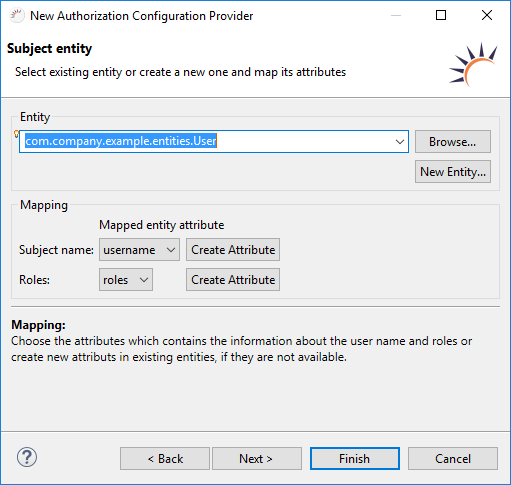
Verknüpfung von User und Roles
- Tabelle für die Benutzer (User) bereits vorhanden - Wählen Sie Ihr bereits vorhandenes User Entity aus.
Noch kein User Entity vorhanden - Klicken Sie auf New Entity... um ein neues Entity User anzulegen. - Wählen Sie bei Mapping > Subject name das Attribut für den Benutzernamen aus.
- Klicken Sie bei Mapping > Roles auf Create Attribute, um das Entity User mit einem Attribut zu erweitern, das die Entities User und Roles miteinander verknüpft.
- Klicken Sie auf Finish.
Optionen:
Subject name - Auswahl des Attributs für den Benutzernamen.
Roles - Auswahl des Attributs mit der Liste (Set/List) aller Rollen eines Benutzers.
Ergebnis:
Project Management > Entities
Role - Die Entity-Klasse Role.java wird um das Attribut users erweitert.
Entity Attribute Datentyp Role name String resources Set / List childRoles Set / List parentRoles Set / List users Set / List User - Die Entity Klasse User.java wird um das Attribut roles erweitert.
Entity Attribute Datentyp User username String password byte[] roles Set / List
Project Management > Data Access - Es wird die DAO-Klasse RoleDAO.java generiert. Bei Auswahl eines bereits existierenden Entities wird kein neues DAO generiert.
Project Management > Business Objects - Es wird die Klasse ExampleAuthorizationProvider.java generiert.
package com.company.example.business; import com.company.example.entities.Resource; import com.company.example.entities.Role; import com.company.example.entities.User; import com.xdev.security.authorization.AuthorizationConfiguration; import com.xdev.security.authorization.AuthorizationConfigurationProvider; import com.xdev.security.authorization.jpa.JPAAuthorizationConfigurationProvider; public class ExampleAuthorizationConfigurationProvider implements AuthorizationConfigurationProvider { private static ExampleAuthorizationConfigurationProvider INSTANCE; public static ExampleAuthorizationConfigurationProvider getInstance() { if (INSTANCE == null) { INSTANCE = new ExampleAuthorizationConfigurationProvider(); } return INSTANCE; } private JPAAuthorizationConfigurationProvider provider; private ExampleAuthorizationConfigurationProvider() { } @Override public AuthorizationConfiguration provideConfiguration() { if (this.provider == null) { this.provider = new JPAAuthorizationConfigurationProvider(User.class, Role.class, Resource.class); } return this.provider.provideConfiguration(); } }
Datenbanktabellen anlegen
Für die neu generierten Entities User, Role und Resource müssen entsprechende Tabellen in der Datenbank angelegt werden.
Entity > Datenbank Export (Create tables)
Default-Daten eingeben
Es ist hilfreich für die Datenbanktabellen USER, ROLE und RESOURCE einige Default-Daten einzugeben.